Developed by: Priscilla Laws with contributions from Robert Boyle, Patrick Cooney, Kenneth Laws, John Luetzelschwab, David Sokoloff and Ronald Thornton


middle schoolhigh schoolintro collegeinter-mediateupper levelgrad school other

calc based
alg based








Overview
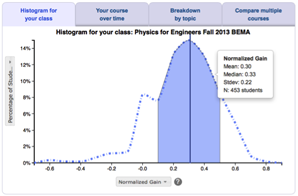
What? A calculus-based intro physics curriculum designed to completely replace traditional lectures and labs with sequenced activities. Students work in groups to make and discuss predictions and observations, and to perform data acquisition, visualization, analysis, and mathematical modeling.
Why not? Materials are only available for the second semester of intro physics. This is a band-aid on a traditional lecture course structure, which is less ideal than making a more drastic change to your course structure and engaging students in working on longer and more meaningful problems.
Topic outline
MODULE 1: The Core Volume: Mechanics I: Kinematics and Newtonian Dynamics (Units 1-7)
Unit 1. Introduction and Computing.
Unit 2. Measurement and Uncertainty.
Unit 3. One Dimensional Motion I—A Graphical Description.
Unit 4. One-Dimensional Motion II—A Mathematical Description of Constant Acceleration.
Unit 5. One-Dimensional Forces, Mass, and Motion.
Unit 6. Gravity and Projectile Motion.
Unit 7. Applications of Newton's Laws.
MODULE 2: Mechanics II: Momentum, Energy, Rotational and Harmonic Motion, and Chaos (Units 8 - 15)
Unit 8. One-Dimensional Collisions.
Unit 9. Two-Dimensional Collisions.
Unit 10. Work and Energy.
Unit 11. Energy Conservation.
Unit 12. Rotational Motion.
Unit 13. Rotational Momentum and Torque as Vectors.
Unit 14. Harmonic Motion.
Unit 15. Oscillations, Determinism, and Chaos.
MODULE 3: Heat Temperature and Nuclear Radiation: Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory, Heat Engines, Nuclear Decay, and Random Monitoring (Units 16 - 18 and 28)
Unit 16. Temperature and Heat Transfer.
Unit 17. The First Law of Thermodynamics.
Unit 18. Heat Engines.
Unit 28. Radioactivity and Radon.
MODULE 4: Electricity and Magnetism (Units 19-27)
Unit 19. Electric Fields.
Unit 20. Electric Flux and Gauss' Law.
Unit 21. Electrical and Gravitational Potential.
Unit 22. Batteries, Bulbs, and Current Flow.
Unit 23. Direct Current Circuits.
Unit 24. Capacitors and RC Circuits.
Unit 25. Electronics.
Unit 26. Magnetic Fields.
Unit 27. Electricity and Magnetism.
Student skills developed
- Conceptual understanding
- Lab skills
- Using multiple representations
- Designing experiments
- Problem-solving skills
- Metacognition
Instructor effort required
- Medium
Resources required
- TAs / LAs
- Projector
- Computers for students
- Advanced lab equipment
- Cost for students
- Tables for group work
Resources
Teaching Materials
Workshop Physics is available in a series of books published by Wiley:
- Module 1: The Core Volume: Mechanics I: Kinematics and Newtonian Dynamics (Units 1-7)
- Module 2: Mechanics II: Momentum, Energy, Rotational and Harmonic Motion, and Chaos (Units 8 - 15)
- Module 3: Heat Temperature and Nuclear Radiation: Thermodynamics, Kinetic Theory, Heat Engines, Nuclear Decay, and Random Monitoring (Units 16 - 18 and 28)
- Module 4: Electricity and Magnetism (Units 19-27)
Research
This is the third highest level of research validation, corresponding to:
- at least 1 of the "based on" categories
- at least 1 of the "demonstrated to improve" categories
- at least 1 of the "studied using" categories
Research Validation Summary
Based on Research Into:
- theories of how students learn
- student ideas about specific topics
Demonstrated to Improve:
- conceptual understanding
- problem-solving skills
- lab skills
- beliefs and attitudes
- attendance
- retention of students
- success of underrepresented groups
- performance in subsequent classes
Studied using:
- cycle of research and redevelopment
- student interviews
- classroom observations
- analysis of written work
- research at multiple institutions
- research by multiple groups
- peer-reviewed publication
References
- R. Beichner, The impact of video motion analysis on kinematics graph interpretation skills, Am. J. Phys. 64 (10), 1272 (1996).
- P. Laws, Millikan lecture 1996: Promoting active learning based on physics education research in introductory physics courses, Am. J. Phys. 65 (1), 14 (1997).
- P. Laws, P. Rosborough, and F. Poodry, Women's responses to an activity-based introductory physics program, Am. J. Phys. 67 (S1), S32 (1999).
- P. Laws and R. Thornton, FIPSE Interactive Physics Project (October 1989-August 1993). Final report, 1993.
- P. Laws, M. Willis, and D. Sokoloff, Workshop Physics and Related Curricula: A 25-Year History of Collaborative Learning Enhanced by Computer Tools for Observation and Analysis, Phys. Teach. 53 (7), 401 (2015).
- E. Redish, Teaching Physics with the Physics Suite (John Wiley & Sons Inc., Somerset, 2003).
- E. Redish, J. Saul, and R. Steinberg, Student expectations in introductory physics, Am. J. Phys. 66 (3), 212 (1998).
- E. Redish, R. Steinberg, and J. Saul, On the effectiveness of active-engagement microcomputer-based laboratories, Am. J. Phys. 65 (1), 45 (1997).
- J. Saul and E. Redish, Evaluation of the Workshop Physics Dissemination Project, 1998.
- D. Sokoloff, Teaching Electric Circuit Concepts Using Microcomputer-Based Current/Voltage Probes, presented at the NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Microcomputer-Based Laboratories, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 1992.
- R. Thornton, Conceptual Dynamics: Following Changing Student Views of Force and Motion, presented at the International Conference on Undergraduate Physics, College Park, MD, 1996.
- R. Thornton and D. Sokoloff, Assessing student learning of Newton's laws: The Force and Motion Conceptual Evaluation and the Evaluation of Active Learning Laboratory and Lecture Curricula, Am. J. Phys. 66 (4), 338 (1998).